Kortikale Und Subkortikale Areale
While this is an important part of the brain it is only the surface. Cortical stroke may present with a gaze preference.
Https Docserv Uni Duesseldorf De Servlets Derivateservlet Derivate 50904
In the human brain it is between two and three or four millimetres thick and makes up 40 per cent of the brains mass.
Kortikale und subkortikale areale. Subcortical structures and functions so far we have examined mostly the large visible areas on the surface of the brain. It is rare for a subcortical stroke to impair vision. This occurs when the frontal eye fields responsible for horizontal gaze are infarcted.
In this presentation we will identify the location and function of different brain areas and how the parts interact. The location of motor areas of the cerebral cortex and their parallel and hierarchical projections to the brain stem and spinal cord. They are involved in complex activities such as memory emotion pleasure and hormone production.
As adjectives the difference between subcortical and cortical is that subcortical is medicine of or pertaining to the subcortex the portion of the brain located below the cerebral cortex while cortical is anatomy pertaining to the outer layer of an internal organ or body structure such as the kidney or the brain. Somatotopic representation in the primary somatosensory and motor areas. This pathology is characterized by affecting specific regions of the brain which is why it can be divided between cortical atrophy and subcortical atrophy.
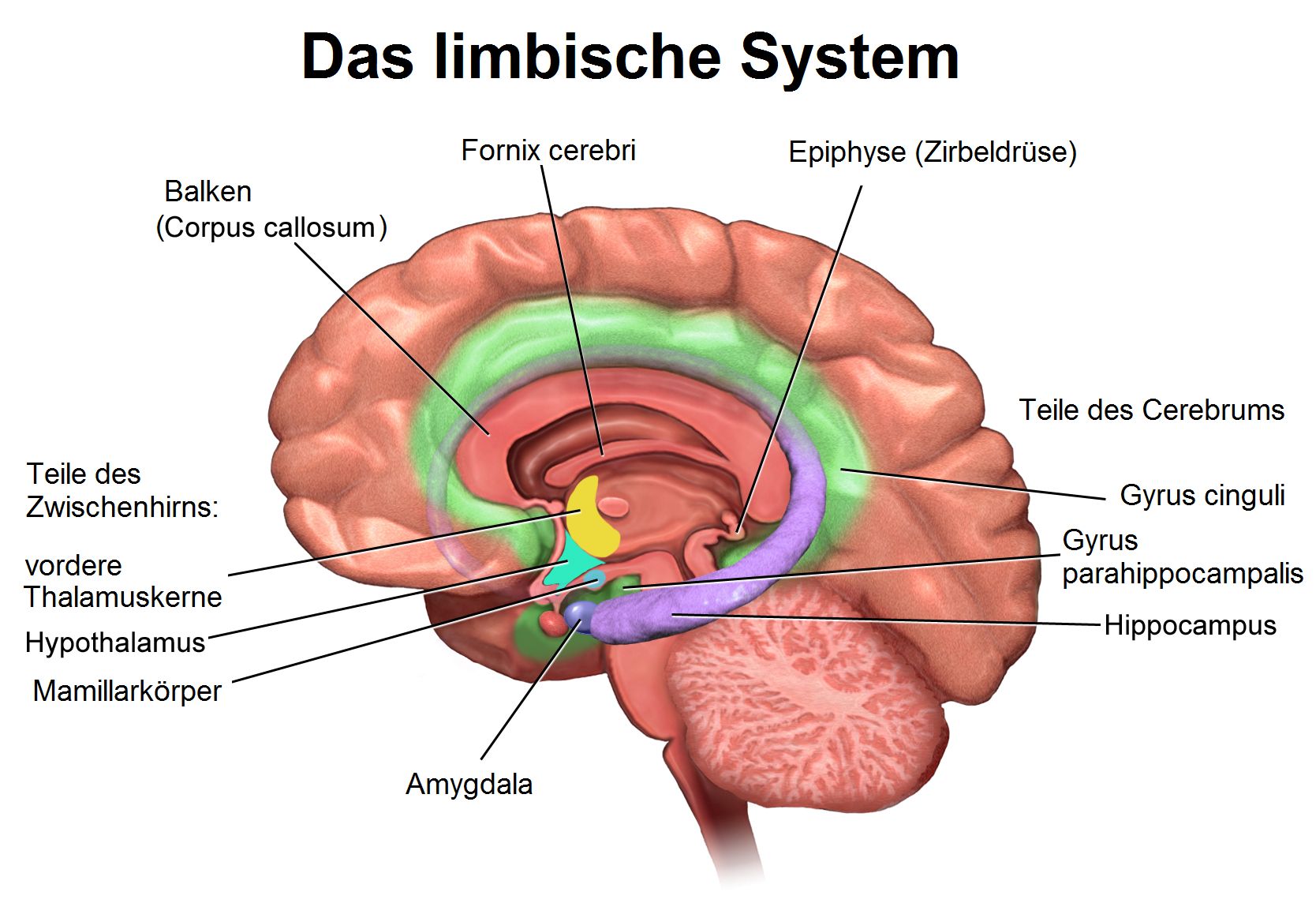
The limbic system also known as the paleomammalian cortex is a set of brain structures located on both sides of the thalamus immediately beneath the medial temporal lobe of the cerebrum primarily in the midbrain. The skin is analogous to the cerebral cortex the fleshy part is the deep white matter and the stone represents the subcortical structures. The primary visual area and its connected association areas which have different functions.
All types of dementia also known as a major neurocognitive disorder cause impairments in memory reasoning and judgment. Depending on which part of the brain is suspected as the primary location of the dementia the type of dementia may be classified as either cortical or subcortical. The cerebral cortex is the outer covering of the surfaces of the cerebral hemispheres and is folded into peaks called gyri and grooves called sulci.
The cerebral atrophy is a neurological condition characterized by the progressive death of brain neurons. For example a right cortical stroke will result in a patients eyes being deviated to the right side. Subcortical structures are a group of diverse neural formations deep within the brain which include the diencephalon pituitary gland limbic structures and the basal ganglia.
The classification of structures as part of the limbic system is historical and originates from the position. The interconnections of the thalamus and cortex. The result is that the patients eyes will deviate to the side of the stroke.
Subcortical is a derived term of cortical.

Grosshirnrinde Cortex Cerebri Aufbau Und Funktionelle Gliederung

Vaskulare Demenz Enzephalopathie Lebenserwartung Verlauf
2

Calameo Das Menschliche Gehirn Fur Dummies
2

4 1 Emotionen Flashcards Quizlet
Gehirn Atlas Endhirn Grosshirn Telencephalon Cerebrum
Limbisches System Wikipedia
14 Limbisches System