Cortical Region Of Lymph Node
It then runs through cortical sinuses into medullary sinuses and leaves through the efferent lymphatic vessels at the hilium as efferent lymph. The hilum is a linear echogenic non shadowing structure that contains the nodal vessels and it appears continuous with the fat around the node.

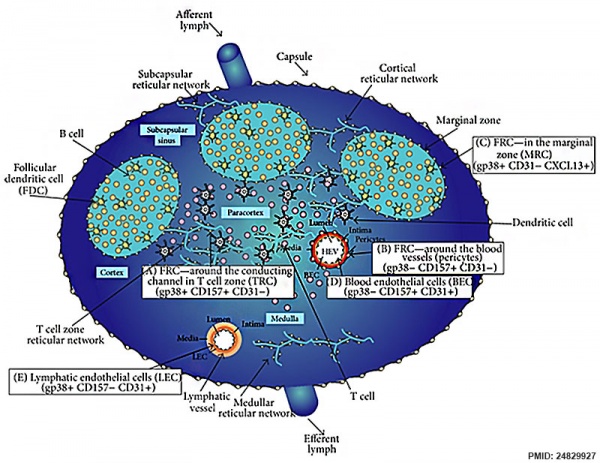
Fibroblastic Reticular Cells Control Conduit Matrix Deposition
In localized axillary lymphadenopathy disease of the lymph nodes the enlargement is restricted to lymph nodes in the axillary areas both arm pits.
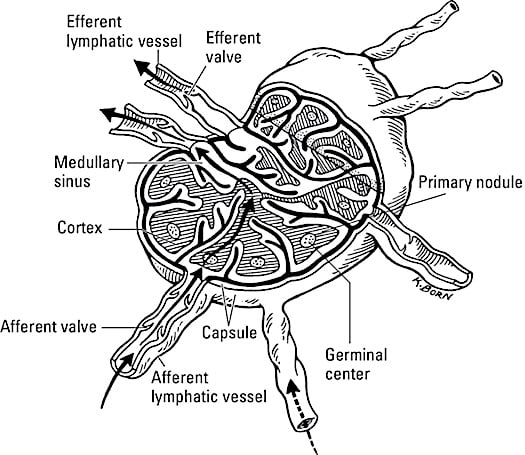
Cortical region of lymph node. Lymph nodes are small nodules of lymphoid tissue found in the course of smaller lymphatics. In the absence of immune stimulation the cortical lymphoid follicles are primary follices composed of small b lymphocytes which may be virgin b lymphocytes or recirculating memory b cells. Underlying the capsule is the cortex a region containing mostly inactivated b and t lymphocytes plus numerous accessory cells such as dendritic cells and macrophages.
Causes of axillary arm pit lymph node enlargement. Lymph nodes usually swell in response to a part of the body that is infected. The cell that dominates the deep cortical region of a lymph node is the cell.
The capsule is an outer layer of connective tissue. Lymph nodes range in diameter from. The cortex is further divided into two functional areas.
Occipital lymph nodes that swell may be an indication that you have a certain infection of the scalp or other neighboring regions. The number and composition of follicles can change when challenged by an antigen. A lymph node is divided into compartments called lymph nodules or lobules each consisting of a cortical region of combined follicle b cells a paracortical region of t cells and a basal part of the nodule in the medulla.
The outer cortex and inner cortex or paracortex. The nodes are oval or reniform in shape 1 25 mm long and light brown black pulmonary or creamy white intestinal in color. Within the node there is generally a hypoechoic marginal zone which can be distinguished from the central hyperechoic hilar region the medullary sinuses with blood vessels and efferent lymph vessels.
Superficial lymph nodes particularly in the head and neck axilla and inguinal regions are amenable to ultrasound us evaluation. These infections can be bacterial or viral in origin. The medulla of a lymph node contain lymphocytes and plasma cells.
Lymph nodes in the neck are oval or ellipsoid in shape. 1 mm to 25 mm. The lymph passes through one or more lymph nodes before reaching the larger lymph trunks.
Each lymph node is divided into two general regions the capsule and the cortex. Harder fixed or matted axillary nodes often indicate malignancy usually from the lung or breast. Dividing lymphocytes can be found in the of the lymphoid nodule.
A normal lymph node is ovoid in shape hypoechoic to the adjacent muscle and frequently contains an echogenic fatty hilum fig. Lymph containing micro organisms soluble antigens antigen presenting cells and a few b cells enters the lymph node via afferent lymphatic vessels which enter the subcapsular sinus. The lymph node cortex beneath the subcortical sinus the location of primary and secondary lymphoid follicles a.
Ch 3 Pathology Of Lymph Nodes

Anatomy Of The Lymphatic And Immune Systems Anatomy And
Lymph Node Development Embryology

Material Design For Lymph Node Drug Delivery Nature Reviews
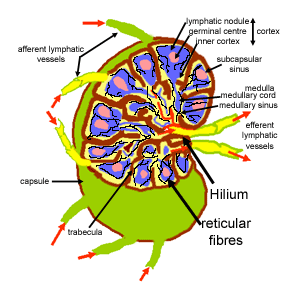
The Histology Guide Lymphoid
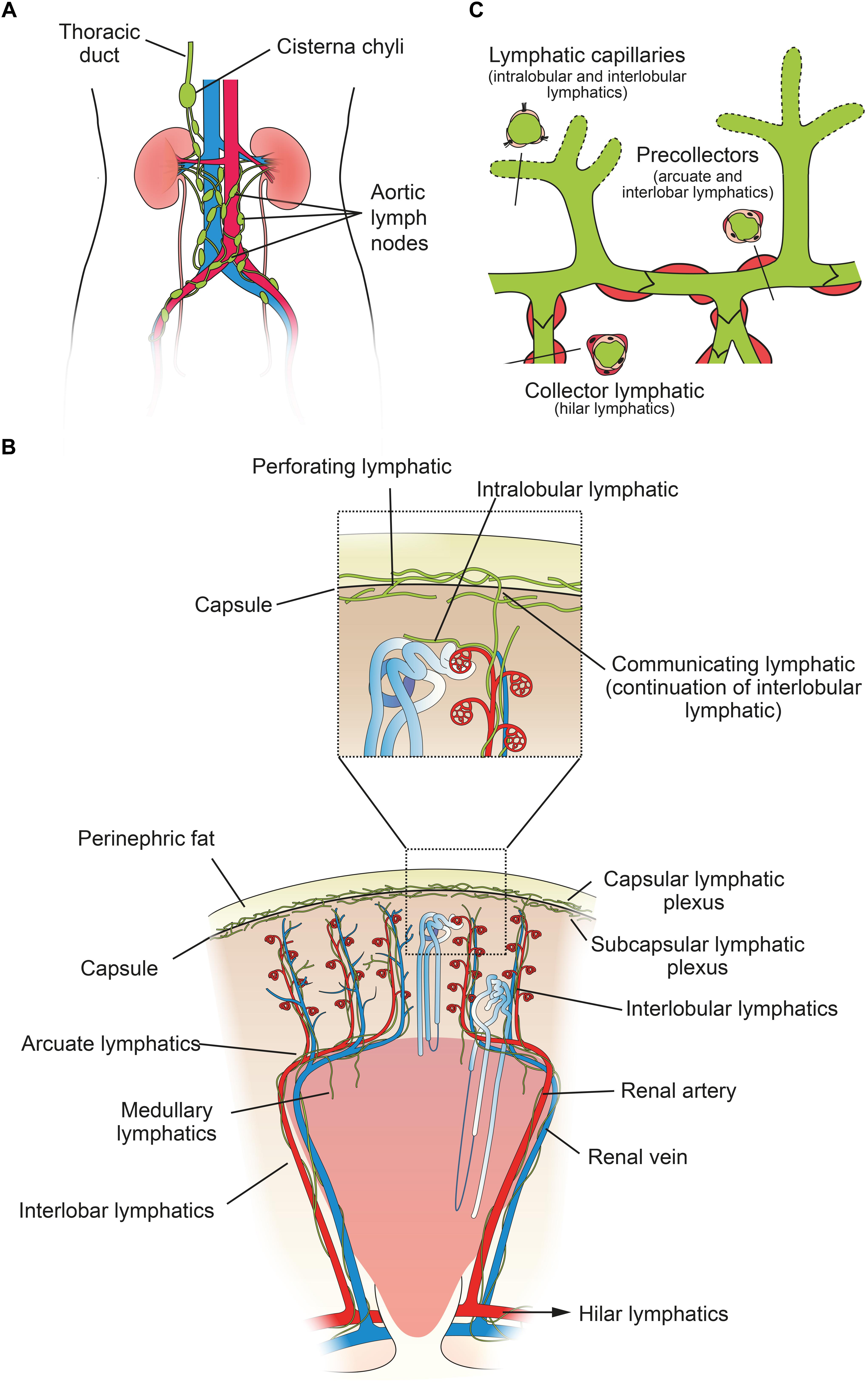
Frontiers Renal Lymphatics Anatomy Physiology And Clinical
Lymph Node

How Lymph Nodes Work Dummies

Lymph Node Anatomy Pictures And Information