Kortikale Reorganisation Amputation
The mechanisms involved are likely to include reduction of gabaergic inhibition. Amputation is a striking driver of plasticity as it induces both sensory deprivation and altered behaviour.

Phantom Limb Pain Pain Matters
Lastly it is possible that the level of individual prosthetic use after amputation may have contributed to the expression of cortical reorganization.
Kortikale reorganisation amputation. This study was undertaken to identify evidence of cortical reorganization in lower limb amputees and to find evidence for the pain memory theory. Our findings suggest that motor reorganization after lower limb amputation occurs predominately at the cortical level. The human motor system undergoes reorganization after amputation but the site of motor reorganization and the mechanisms involved are unknown.
Cortical reorganization and pain memory are theories to explain phantom limb pain and other postamputation phantom phenomena. On the basis of the demonstration of substantial plasticity of the. Brain reorganization is a key mechanism that enables adjustment to novel situations and injuries but it had also been suggested to have maladaptive consequences flor et al 2006.
Flor and birbaumer 2000. The part of the brain that is in charge of the amputated lim. His main focus is on the perceptual correlates of cortical reorganization.
Kortikale reorganisation und schmerz. Every part of the body is connected to a corresponding area in the brain which creates a cortical map. While subject a1 only used a cosmetic prosthetic subjects a2 and a3 both used myoelectric prosthetics and it is not possible to quantify the extent of which this affected cortical representations without controlled longitudinal studies.
Cortical remapping also referred to as cortical reorganization is the process by which an existing cortical map is affected by a stimulus resulting in the creating of a new cortical map. It is possible that different relationships between pain and cortical reorganization exist in recently amputated subjects or subjects with long standing pain as compared with no long standing pain before the amputation pascual leone et al 1996. Cortical reorganization remained unchanged in three plp amputees whose pain was not reduced by brachial plexus blockade and in the phantom pain free amputation controls though the actual peripheral manipulation was the same in all subjects.
Although phantom limb pain is a frequent consequence of the amputation of an extremity little is known about its origin1 4. When something happens to disrupt the cortical maps such as an amputation or a change in neuronal characteristics the map is no longer relevant. The modulation of plasticity and phantom limb pain by anesthesiological interventions is described and the results of preemptive analgesia for the prevention of phantom limb.
Pain that incorporates both peripheral and central factors and assigns an important role to chronic pain before the amputation. Several lines of research over the last decade have shown that the representation of the body surface in the somatosensory cortex changes in response to changes in peripheral input after amputation or deafferentation as well as after overstimulation.
Frontiers Reorganization Of The Injured Brain Implications For
Https Www Db Thueringen De Servlets Mcrfilenodeservlet Dbt Derivate 00046056 Dissblume Pdf

Pdf Mirror Therapy In Lower Limb Amputees A Look Beyond Primary
Https Content Iospress Com Download Restorative Neurology And Neuroscience Rnn00282 Id Restorative Neurology And Neuroscience 2frnn00282
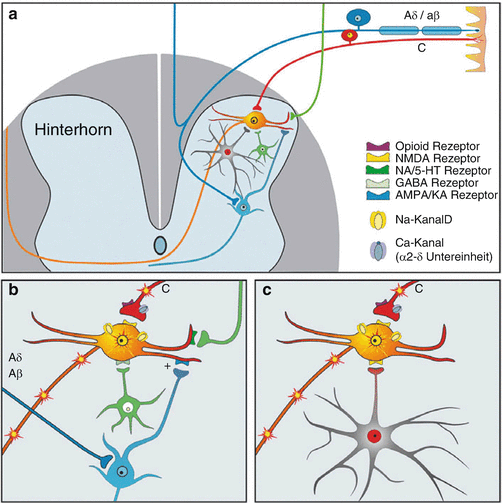
Schmerzentstehung Bildgebung Und Schmerzmessung Springerlink
Pdf Single Stage Osseointegrated Reconstruction And
Https Pdfs Semanticscholar Org 417a Db19ab539f3121c8e657bef3a565104332d4 Pdf

Pdf Capsaicin 8 Patch Treatment For Amputation Stump And Phantom

Pdf Kortikale Reorganisation Und Schmerz Wolfgang Larbig